BLOG ARTICLE
Generative Engine Optimization (GEO) - How to optimize for AI search in 2025
Last updated: 4/13/2025
Last updated: 4/13/2025
In 2025, AI-powered tools like ChatGPT, Google AI Overviews, and Perplexity are transforming how people find information online. Instead of scrolling through a bunch of links, users now get instant, personalized answers generated by artificial intelligence.
That means traditional SEO isn’t enough anymore.
If you want your content to show up in these AI-driven searches, you need to embrace something new: Generative Engine Optimization (GEO).
GEO is all about making sure your content is optimized for AI platforms, so it gets noticed, understood, and featured.
In this guide, I’ll break down what GEO is, why it’s so important, and how you can start using it to stay ahead of the competition.
Let’s dive in!
Is GEO the future (and SEO dead?)
SEO Isn’t Dead. It’s Just No Longer Enough.
GEO is the next chapter in the SEO playbook... not a rewrite, but an upgrade.
Traditional SEO helps you rank on Google by building authority (like earning backlinks) and targeting keywords. GEO does something similar but with a twist: it optimizes your content for AI’s eyes, not just Google’s algorithm.
Yes, backlinks and domain authority still matter, they’re your ticket to being seen as trustworthy.
But GEO goes further. It’s about structuring your content so clearly, answering questions so precisely, and citing data so compellingly that AI systems like ChatGPT or Google AI Overviews can’t help but quote you.
Here’s the difference:
- SEO gets you ranked.
- GEO gets you cited by AIs that better undertstand needs and contexts.
For example, a post like “Fix a Leaky Faucet” might rank on Google with good backlinks, for that particular keyword.
But with GEO, you’d structure it as “Step-by-Step Fixes for a Leaky Kitchen Faucet (no experience needed)”—packed with numbered steps, tool lists, and plumber quotes. AI loves this. It’s not about replacing SEO; it’s about enhancing it.
Because in AI search, even the best-ranked page won’t win if robots can’t snatch precise answers from it in seconds.
So when AI answers a query, it’s not magic—it’s a two-step dance between old-school authority and next-gen clarity.
First, AI plays gatekeeper.
Before it even considers your content, it checks if you’re “trusted.” How?
- Backlinks/mentions: If reputable sites like The New York Times or TechCrunch link or mention to you, you pass the sniff test.
- Domain authority: Established brands (think HubSpot or Healthline) get a fast pass.
- Freshness: A 2024 guide beats a dusty post from 2015.
This is why giants like Forbes dominate AI answers—they’ve spent years mastering SEO basics.
But here’s where it gets interesting.
Once you’re in the door, AI races through your content, hunting for three things:
- Instant clarity: Can it find answers in seconds? Headers, bullet points, and FAQs win.
- Razor-sharp specificity: Do you mention exact tools, products, or studies? Do you answer specific questions precisely?
- Zero fluff: No vague claims—just actionable, data-backed advice.
This is the GEO advantage.
How to do GEO and show up on AI answer engines - Actionable tips
1. Optimize for AI Search by Crafting Content Around Real-World Questions
AI thrives on answering hyper-specific, conversational questions. Think about how people actually ask for help: “How do I fix a leaky faucet without calling a plumber?” or “What’s the healthiest breakfast for someone with IBS?”
Here’s how to do it:
-
Step 1: Use tools like AlsoAsked.com to uncover the long-tail questions people ask around your topic. For example, if you run a fitness blog, search “yoga for back pain” and find follow-up questions like, “Can yoga fix a herniated disc?” or “What poses should I avoid with sciatica?”
-
Step 2: Turn those questions into H2 headers. Instead of a generic “Yoga Benefits” post, structure your content as:
- “Can Yoga Fix a Herniated Disc? What Experts Say”
- “5 Safe Yoga Poses for Sciatica Relief (Step-by-Step Guide)”
- “3 Yoga Mistakes That Worsen Back Pain”
-
Step 3: Answer each question concisely in 2-3 sentences at the top of each section. AI scanners prioritize clear, direct answers.
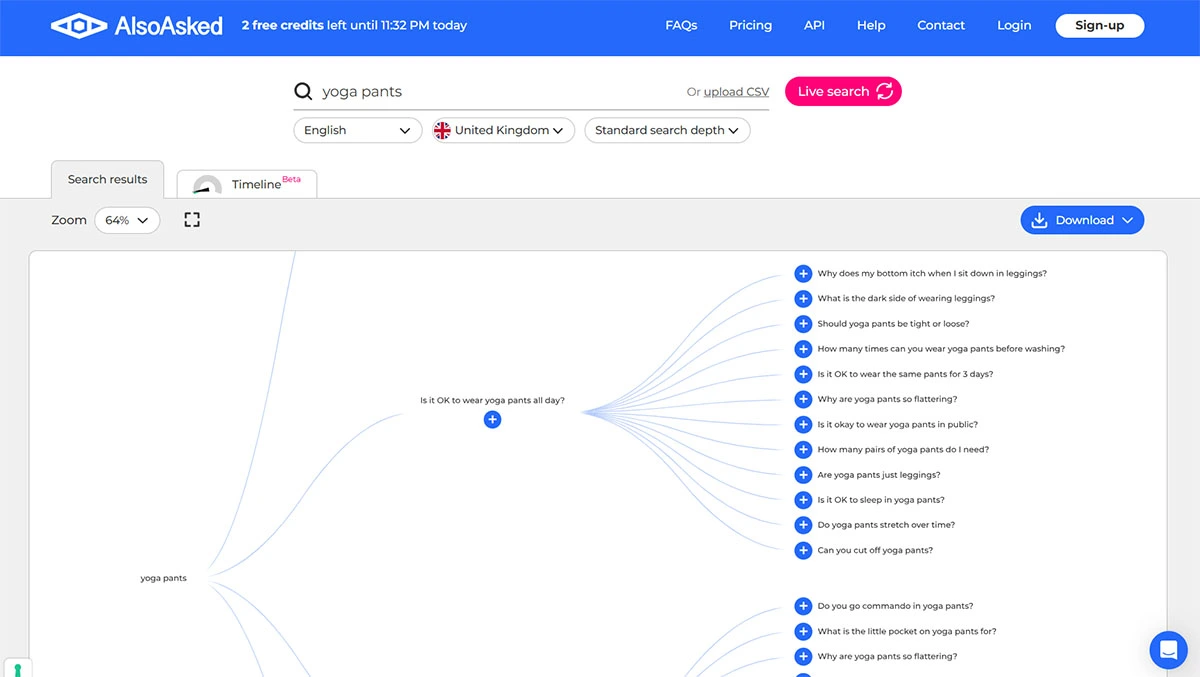
AI tools like Perplexity scrape forums, Reddit, and Q&A sites to learn how people phrase questions. By mirroring this language, you signal to AI that your content matches real-world queries.
2. Help AI Understand Your Content: Context and Entities
AI doesn’t just read—it analyzes context.
For example, if you mention “Apple,” it needs to know if you’re talking about the fruit, the tech giant, or the Beatles’ label.
Without clarity, your content risks being misinterpreted or overlooked entirely.
This is why context matters. AI relies on precise signals to correctly interpret and prioritize your content. The clearer you are about the entities you’re referencing—like people, brands, places, or products—the easier it is for AI to present your content as the best answer.
Here’s how you can help AI understand your content better:
Here’s how to do it:
-
Step 1: Identify key entities in your content (people, brands, places, products). Use tools like Google’s Natural Language API to auto-detect entities.
-
Step 2: Link entities to authoritative sources. For example:
- “Brooks Adrenaline GTS 23 (view on Amazon)” → Links to product pages.
- “Dr. Jane Smith, a podiatrist at Harvard Medical School, recommends…” → Links to her profile or study.
-
Step 3: Add schema markup to define entities. For a product page, use JSON-LD code like this:
<script type="application/ld+json"> { "@context": "https://schema.org", "@type": "Product", "name": "Brooks Adrenaline GTS 23", "description": "Podiatrist-recommended running shoe for flat feet.", "brand": { "@type": "Brand", "name": "Brooks" } } </script>
Schema markup acts as a “translation layer” for AI, telling crawlers exactly what your content is about, boosting your chances of being cited.
3. Speed Is the New SEO (Here’s How to Fix It)
AI crawlers are impatient.
If your site takes longer than 3 seconds to load, they’ll bounce—and your content gets ignored.
Here’s how to do it:
-
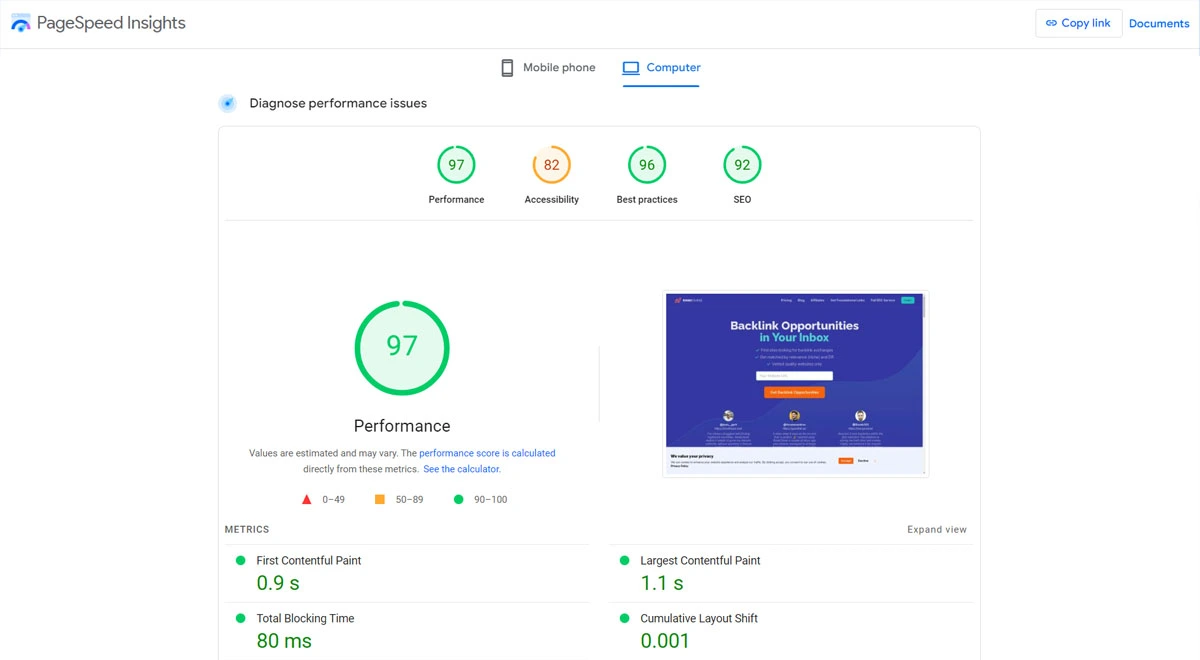
Step 1: Run a speed test using Google PageSpeed Insights. Focus on “Core Web Vitals” like Largest Contentful Paint (LCP).
-
Step 2: Compress images with ShortPixel. For example, a 4MB header image can be reduced to 200KB without quality loss.
-
Step 3: Enable lazy loading for images and videos. If you use WordPress, plugins like WP Rocket do this automatically.
-
Step 4: Use a CDN like Cloudflare. This stores your site’s static files (CSS, images) on servers worldwide, reducing load times for users in different regions.
4. Dominate the “Invisible” Platforms
AI doesn’t just crawl websites—it scrapes Reddit threads, YouTube descriptions, and even LinkedIn posts.
Here’s how to do it:
-
Step 1: Turn blog posts into YouTube tutorials. For example, if you wrote “10 SEO Tips for 2024,” film a 5-minute video summarizing the tips. Upload it with:
- A keyword-rich title: “SEO in 2024: 10 Tactics That Actually Work (Backed by Data)”
- A detailed description: Include timestamps, key takeaways, and links to your blog.
- A transcript: Paste the full script in the description (AI crawlers index this).
-
Step 2: Answer questions on Reddit and Quora. For example, if you’re a SaaS company:
- Search Reddit for “best project management tools for remote teams”
- Write a detailed reply: “At [Your Company], we use ClickUp for X, but here’s a comparison with Asana and Trello…”
- Link to a free tool or guide on your site (no hard selling).
-
Step 3: Repurpose your content into LinkedIn posts and articles. For example, we typically summarize our articles and share the most actionable tips as LinkedIn posts, while publishing the full articles as LinkedIn articles. Interestingly, these LinkedIn articles often rank higher than the original articles on our website.
AI tools like Perplexity prioritize content that’s cited across multiple platforms. By appearing in YouTube transcripts and Reddit threads, you become a “verified” source.
5. The GEO Checklist: 4 Steps to Future-Proof Your Content
Step 1: Audit Like an AI
Use MarketMuse to analyze your content’s depth. It grades articles on factors like:
- Entity coverage: Are you mentioning all relevant people, brands, and terms?
- Semantic relevance: Does your content align with related subtopics?
For example, an article about “email marketing” should cover entities like “open rates,” “A/B testing,” and “GDPR compliance.”
Step 2: Structure for Scanners
- Start with a 50-word “TL;DR” summary at the top.
- Use H2 headers as questions: “What is GEO?”, “Why is GEO Important?”, “How to Implement GEO.”
- Add bullet points, tables, and bold key terms to help AI extract answers quickly.
Step 3: Become a Data Storyteller
Instead of saying “Many businesses succeed with GEO,” say:
“63% of marketers using GEO strategies saw a 2x increase in organic traffic within 6 months (BrightEdge, 2024). For example, SaaS company X grew their AI-driven referrals by 110% by…”
Cite studies, embed charts, or interview experts. Tools like Datawrapper let you create visualizations for free.
Step 4: The “Skyscraper 2.0” Technique
- Find top AI answers: Search your topic on ChatGPT or Perplexity. If the answer cites a study, blog, or tool, note the source.
- Outdo them: If AI cites a “2023 Guide to SEO,” publish a “2024 Ultimate Guide” with video tutorials, expert interviews, and downloadable templates.
- Update old content: Add a section like “2024 Update: How AI Search Changes This Topic.”
Your 30-Day GEO Plan:
- Week 1: Audit 5 key pages with MarketMuse. Fix speed issues.
- Week 2: Optimize 1 pillar post with FAQs and schema markup.
- Week 3: Repurpose that post into a YouTube video and LinkedIn carousel.
- Week 4: Answer 10 questions on Reddit/Quora. Track AI citations with Advanced Web Ranking.
Questions and answers about Generative Engine Optimization (GEO)
What is generative engine optimization?
Generative Engine Optimization (GEO) is the process of optimizing content to ensure it is easily understood and cited by AI-driven search engines like ChatGPT, Google AI Overviews, and Perplexity.
Unlike traditional SEO, which focuses on ranking in search results, GEO helps your content become a trusted source that AI platforms can pull answers from directly.
How to optimise for generative AI
To optimize for generative AI, focus on structuring content in a way that AI can easily process and extract key information. Here’s how:
- Answer specific, conversational questions clearly and concisely.
- Use structured formats like bullet points, step-by-step guides, and FAQs.
- Implement schema markup to help AI understand content context.
- Improve site speed and mobile usability to enhance AI accessibility.
- Distribute content across multiple platforms like YouTube, Reddit, and Quora.
What is the difference between google seo and geo?
Google SEO focuses on ranking web pages in search results by optimizing for factors like keywords, meta tags, backlinks, and technical performance to ensure higher visibility on traditional search engines like Google.
GEO, on the other hand, is designed to optimize content for AI-powered search engines like ChatGPT and Google AI Overviews. While it shares elements with SEO—such as site speed, authority, and user experience—GEO places a greater emphasis on:
- Answering specific queries with clarity and efficiency using structured content (e.g., bullet points, step-by-step guides, and FAQs).
- Providing direct, concise answers that AI can extract and present quickly.
- Ensuring contextual accuracy by structuring content in a way that AI can easily interpret and cite.
- Building credibility and trust through entity recognition and authoritative citations.
Will SEO be taken over by AI
SEO won’t be completely replaced by AI, but it will evolve. AI-driven search is shifting how users find information, prioritizing quick, direct answers instead of long search results. Businesses need to integrate GEO strategies with traditional SEO to stay visible across both AI-driven and traditional search platforms.